

There are so many factors that go into determining different species and their applicable offshoots. Some trees do better around water, while some don’t need it nearly as much. All trees are different, depending on fruit, leaves, bark, or even just the potential for growth or ability to adapt to difficult environments. What Are The Major Differences Between Oak and Maple Trees? As an Amazon Associate, we earn from qualifying purchases. Read also about other forest trees – here are our guides about Oak, Pine, Sycamore.Just to add – when you shop using links from Tree Journey, we may earn affiliate commissions if you make a purchase. Here are our guides on pruning maple trees and saving dying tree. Because maple trees vary so much from species to species, you may want to research specific maple varieties to learn more about the differences between them.Īs a good place to start, check out these videos on sugar maples and red maples. Some maple trees look quite similar to those of other varieties, while some look vastly different and may not be easily recognizable as a maple. Maple leaves and samaras can be eaten as food ( squirrels love them too!). Maple leaves, buds, and bark are used as herbal remedies in some regions.ħ. Some varieties of maple are kept and grown as ornamental trees in landscaping.Ħ. The sap is processed into maple sugar and syrup.ĥ. Instruments, such as violins, are often made of maple wood.Ĥ. Maple wood is commonly used in building, construction, and carpentry.ģ. Sap: The sap from any maple species can be made into syrup.įood: Maple fruits are edible and highly nutritious the leaves, though bitter, can also be eaten and used in herbal remedies.ġ.
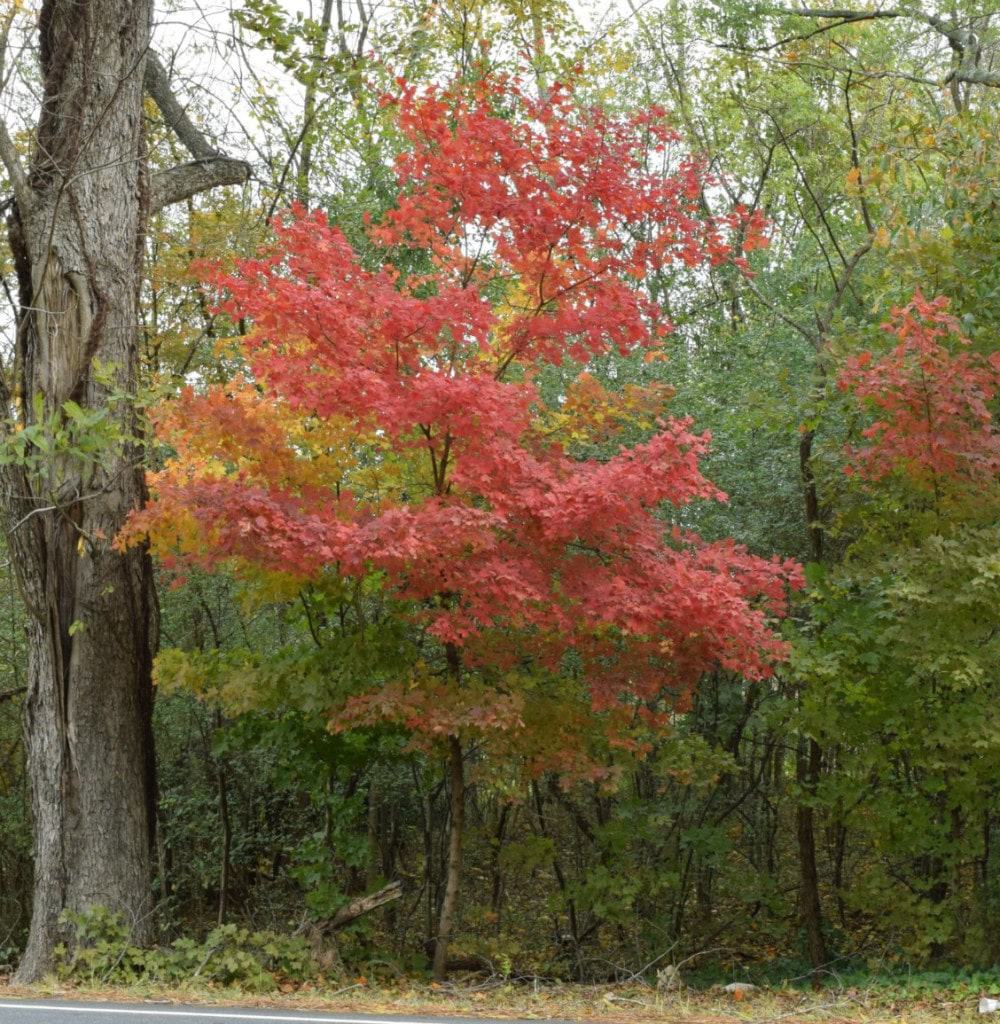

Wood: Maple wood is considered a hardwood whether it’s called “hard maple” or “soft maple.” Silver maples prefer wet conditions and often grow near stream beds, lake shores, and other bodies of water.Īpproximately 130 common species include the sugar, black, red, and silver maples
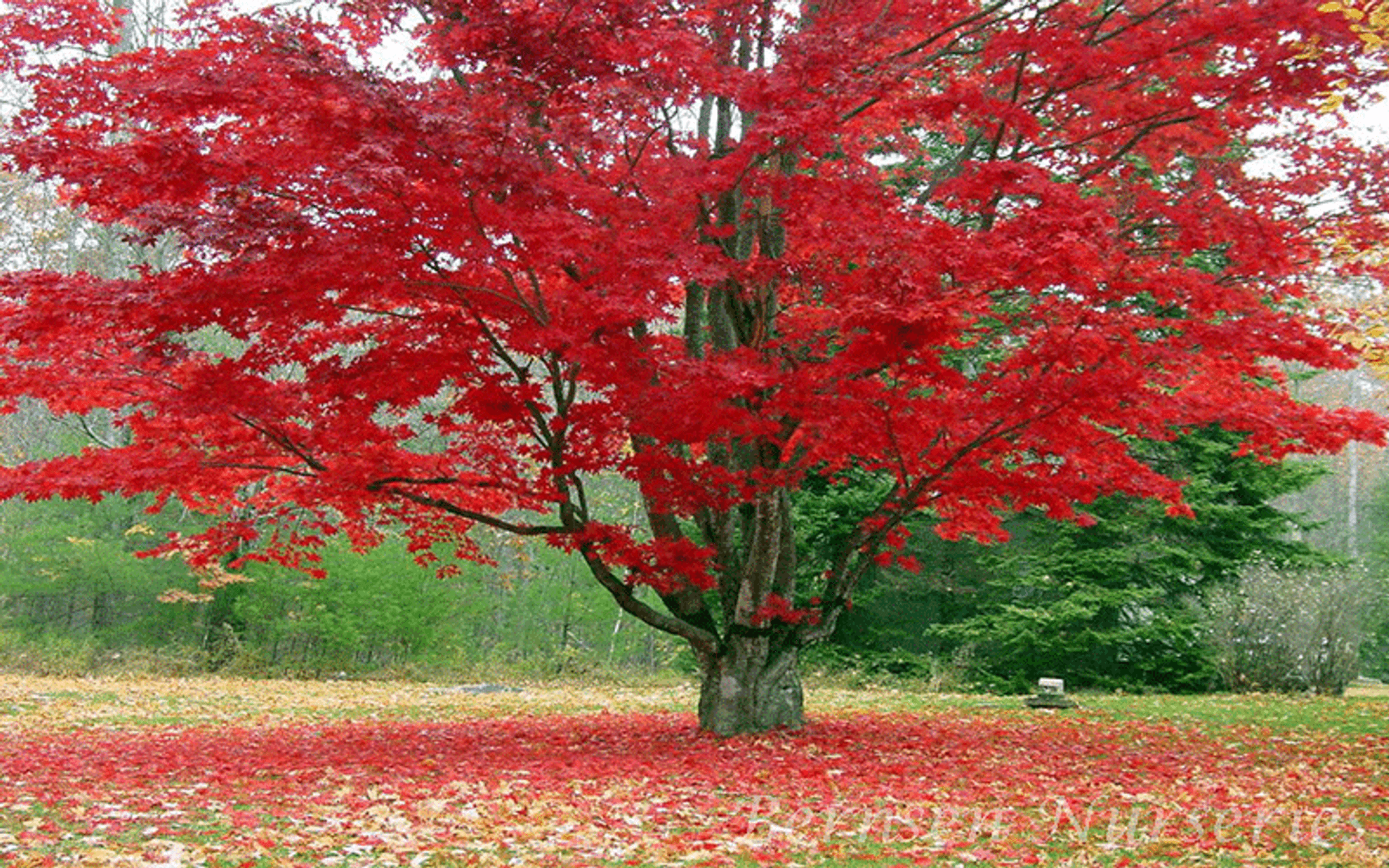
Red maples are highly adaptable to a variety of habitats.Ĥ. Black maples are more adaptable to warm, dry climates than sugar maples.ģ. Sugar maples prefer cool, damp climates and well-drained, loamy, slightly acidic soil.Ģ. Height varies widely by species usually between 20 and 80 feet.ġ30 to 300 years lifespan varies widely by species.Ĭommonly found throughout Asia, North America, and Europe.ġ. Maple bark is generally brown or grayish brown smooth in young trees, the bark becomes rough and ridged as the tree matures. Trees produce small, winged fruits called samaras some ripen in spring, while others ripen in the fall. They have broad, palmate leaves divided into 3 to 5 lobes leaves are light to dark green in summer, red, orange, or yellow in the fall. Check out this table to learn some key facts about maple trees. Did you know that people throughout the world use maple trees to make everything from syrup to violins to herbal remedies? Maples are amazing, useful, and incredibly diverse plants, and they grow well in many different regions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
